Jeolla Province
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Jeolla Province | |
|---|---|
| Korean transcription(s) | |
| • Hangul | 전라도 |
| • Hanja | 全羅道 |
| • Revised Romanization | Jeolla-do |
| • McCune–Reischauer | Chŏlla-do |
 | |
| Country | Joseon |
| Capital | Jeonju |
| Government | |
| • Type | Province |
| Dialect | Jeolla |
Jeolla Province (Korean: 전라도; Hanja: 全羅道, [tɕʌ̹ɭɭa̠.do̞]) was one of the historical Eight Provinces of Korea during the Kingdom of Joseon in southwestern Korea. It consisted of the modern South Korean provinces of North Jeolla, South Jeolla and Gwangju Metropolitan City as well as Jeju Province. The provincial capital was Jeonju, the current capital of North Jeolla. The entire inland region was called Honam (lit. 'south of the lake'), which is still commonly used today.
Jeolla-do, including North and South Jeolla,was the first province/state out of the Eight Provinces system to have its 1000th year anniversary in 2018, as the name 'Jeolla-do' was established in 1018, during Hyeonjong of Goryeo's 9th year in power.[1]
The population of Jeolla-do is 4,973,834 as of January 2024.
History
[edit]Samhan and Samguk
[edit]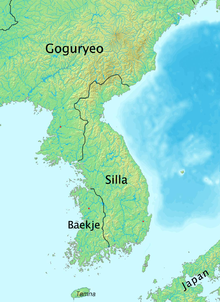
During the Samhan era of Korean history, the area of Jeolla was controlled by the Mahan confederacy and the Tamna kingdom on Jeju. Fifteen of the 45 Korean tribes had their bases in this region. When Baekje overtook Mahan by the 5th century, the Three Kingdoms era began and the region became part of southern Baekje. Jungbang was the center of the province during this period.
Unified Silla
[edit]When Silla conquered Baekje with the help of Tang China in 660, it became a territory of Later Silla during the 16th year of the reign of Munmu of Silla. Silla reorganized this territory into nine ju (주) and five gyeong (경), three of the ju belonging to the former Baekje. The northern territory of former Baekje, Ung (Ungju; 熊州), corresponds to modern-day South Chungcheong Province.
The middle area consisted of Wansan (完山州) and Namwon, which correspond to modern-day North Jeolla. Wansan was later renamed Jeonju. The southern area consisted of Mujin (Mujin-ju), which was renamed Mu (武州) in 757, the 16th year of the reign of Gyeongdeok of Silla. Mu consisted of one gun and 43 hyeon, and corresponds to modern-day South Jeolla.
Goryeo dynasty
[edit]In 983, during the second year of the reign of Seongjong of Goryeo, the country was reorganized into 12 mok. Jeonju became Jeonju-mok (全州牧), while Muju was split into the two mok of Naju and Seungju. In 995, King Seongjong again reorganized the country, this time into 10 do (Korean: 도; Hanja: 道; lit. province). Jeonju-mok was renamed Gangnam-do (lit. 'province south of the river') while Naju and Seungju were reunited and renamed Haeyang-do (lit. 'ocean province').
In 1018, during the 9th year of the reign of Hyeonjong of Goryeo, the country was again reorganized into 5 do, and the provinces of Gangnam and Haeyang were merged to form the province of Jeollaju (全羅州道). The name derived from the names of the principal cities of Jeonju (全州) and Naju (羅州). (The difference between na- and -la is due to the (initial sound rule of modern Korean). This was the first time the area currently known as Jeolla was united under one administrative division, and it would remain this way for nearly eight centuries.
Joseon: 1392–1910
[edit]In 1413, during 13th year of the reign of Taejong of Joseon, the territories were once again reorganized into 8 do. This is the era of the historic Eight Provinces. Jeollaju-do was variously known as Gwangnam, Jeongwang, and Jeonnam, but the original name persisted, and was eventually shortened to simply Jeolla-do (全羅道).
The Donghak Peasant Revolution of 1894–1895 began in Jeolla-do, which was a peasant revolt fueled by the fervor of the believed coming of a local messiah and protests over Seoul's high taxes on rice and the increasing number of Japanese traders in Joseon. There was anti-Japanese sentiment due to the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–1598).
On May 26, 1895, Gojong of Korea replaced the 8 do system with a 23 bu district system and Jeolla was replaced by the districts of Jeonju (Korean: 전주부; Hanja: 全州府; RR: Jeonjubu) in the northwest, Naju (나주부; 羅州府; Najubu) in the southwest, Namwon (남원부; 南原府; Namwonbu) in the east, and Jeju (제주부; 濟州府; Jejubu) on Jeju-do.
On August 4, 1896, Emperor Gojong issued Royal Order 36, repealing the district system and restoring the province system. Jeolla was divided north-south into North Jeolla Province and South Jeolla Province.[2] Also divided were Chungcheong Province, Gyeongsang Province, Hamgyong Province and Pyongan Province, bringing the total to 13 provinces.
Republic of Korea: 1948–present
[edit]North Jeolla Province consisted of the Jeonju and northern Namwon districts, while South Jeolla Province consisted of the southern Namwon districts, Naju district, and Jeju island. Jeonju was retained as the capital of North Jeolla, with Gwangju being made the capital of South Jeolla. The capital of South Jeolla was later moved to Namak in 2005, and Gwangju was designated a Special City.
Geography
[edit]Jeolla Province was bounded on the north by Chungcheong Province, on the east by Gyeongsang Province, on the south by the East China Sea, and on the west by the Yellow Sea. The region is bordered on the east by the Sobaek Mountains and is drained by the Yeongsan, Seomjin and Mangyeong rivers. The largest city in the region is Gwangju. Apart from Jeonju and Naju, other cities of note include Iksan (formerly Iri), Gunsan, Mokpo, Namwon, Suncheon, and Yeosu.
References
[edit]- ^ https://www.jeonbuk.go.kr/index.jeonbuk?menuCd=DOM_000000101004005000
- ^ "History | jeollanamdo". www.jeonnam.go.kr. Retrieved 26 May 2024.
